Feeding your baby

Health Canada, the Canadian Paediatric Society, the World Health Organization, and many others agree that exclusive breastfeeding (or chestfeeding) for the first six months, and continued for up to two years or longer, (with the introduction of solid foods) is important for infants and toddlers:
- nutrition,
- immunologic protection (helps your baby stay healthy and avoid getting sick), and
- healthy growth and development.
Learn about our free infant feeding clinic, offered by registered nurses and lactation consultants.
Making an informed decision about feeding your baby |
|||||||||||||||
| It is important to fully understand the difference between breastmilk (human milk) and formula to make the best decision for your family. However you feed your baby, we are here to support you.
It can be difficult to go back to breastfeeding once you start formula feeding.
|
|||||||||||||||
When to feed your baby
|
|||||||||||||||
|
In the first few months, most babies feed at least eight times in a 24 hour period. This does not mean they feed every three hours. Watch for your baby’s cues and respond to them. Your baby ‘s cues will help you know when they are ready to feed, if they need a break, and when they are finished feeding. When your baby is hungry, they may
Crying is a late sign of your baby’s hunger, and you may find that your baby is more difficult to latch when they are crying. Calm your baby by cuddling, holding them skin-to-skin, rocking, talking, or any other method that works for you. When your baby is full, they may
Feed your baby as often and for as long as your baby wants, responding to their needs. Watch your baby, not the clock. Night time feeds are normal and important, and will last for many months. Babies often cluster feed in the evening, which means they want to feed often for short periods. |
|||||||||||||||
Latching your baby |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Feeding babies formula |
|||||||||||||||
|
Best Start’s Infant formula: What you need to know is available in 18 languages. The booklet provides information on:
For information on how to safely prepare infant formula follow these tips sheets (available in 18 languages). The six tip sheets cover the following topics:
Watch Best Start’s video on how to Safely Preparing Infant Formula for your Baby. |
|||||||||||||||
Know if your baby is getting enough milk |
|||||||||||||||
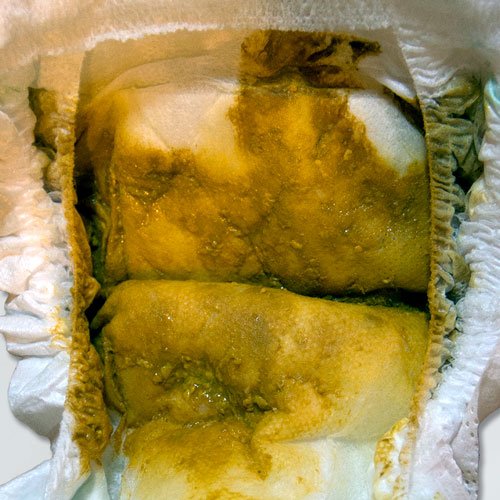
Signs your baby is getting enough milk include:
Your baby should be having at least the number of wet and dirty diapers listed in the chart. If there is poop and pee in one diaper, you can count it as both.
Only count poops that are the size of a toonie, or bigger. If your baby does not have enough wet and dirty diapers, get help right away.
|
|||||||||||||||
Get help right away if your baby does not have enough wet and dirty diapers |
|||||||||||||||
Get help if your baby:
Other signs something is wrong when breastfeeding or chestfeeding:
If you need medical help medical contact your healthcare provider, midwife or Health811 (dial 811).If it is urgent visit:
|
|||||||||||||||
Breastfeeding and chestfeeding supports |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
Expressing and storing breastmilk (human milk) |
|||||||||||||||
|
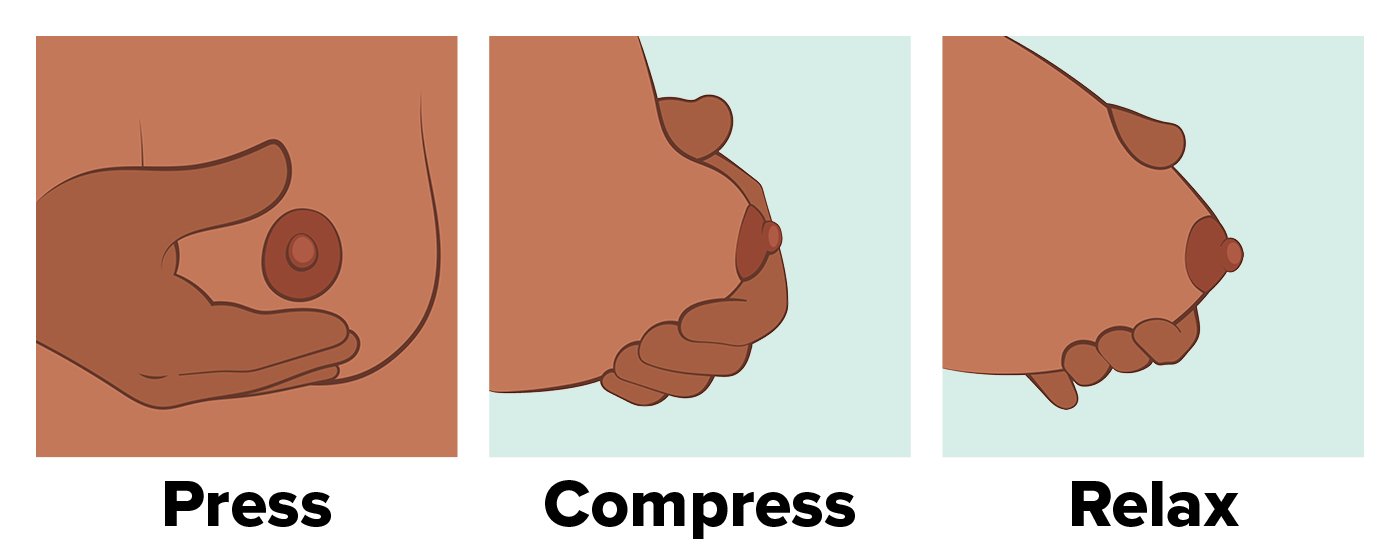
Hand expressing milk allows you to:
How to express milk:
It is normal to not get any milk at first. You may only get a few drops to a teaspoon. This is the perfect amount for your new baby’s small tummy size in those first few days. The more you hand express, the easier it will become, and the more milk you will get. View Best Start’s guidelines for storing breastmilk. View Global Health Media for a video that shows you how to express milk with your hands. View Stanford Medicine’s How to Use Your Hands When You Pump video that demonstrates some ways that pumping mothers can increase production. |
|||||||||||||||
Vitamin D supplement |
|||||||||||||||
|
If your baby is fed breastmilk (human milk)
If your baby is fed formula
|
|||||||||||||||
Feeding in public |
|||||||||||||||
|
In Ontario, all pregnant and breastfeeding parents are protected under the Ontario Human Rights code. Part of this code gives breastfeeding, or chestfeeding, parents the right to feed anytime anywhere without being disturbed, asked to stop, move, or cover up. This includes public areas. Services must also be provided free from discrimination. |
|||||||||||||||
Taking birth control while breastfeeding or chestfeeding |
|||||||||||||||
|
You can take birth control when breastfeeding or chestfeeding. Talk to your health care provider to choose a method that is right for you. Breastfeeding itself can be a form of birth control. This method is called Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM) and can reduce the chance of pregnancy by 98%, but only if you following statements are current:
If any of the statements are not current, the chance of pregnancy increases greatly, you will need to use another form of birth control. The effectiveness of LAM in exclusively pumping mothers may not be equivalent to direct breastfeeding.
Sex and U has additional information on birth control options and effectiveness. Visit the Infant Risk Center’s for additional information on Safe Use of Birth Control While Breastfeeding. The Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada also have additional information on Medications and Drugs While Breastfeeding. |
|||||||||||||||
Substance use (alcohol, tobacco, cannabis) can be harmful when breastfeeding or chestfeeding |
|||||||||||||||
SmokingSmoking can expose you and your child to harmful chemicals. Smoking can cause your baby to be fussy and can decrease the amount of milk you make. Babies and children are especially vulnerable to the effects of smoke; if you can, try to cut down on smoking or quit. If you or someone else in your home smokes, decrease your baby’s exposure to second-hand smoke. Here are a few ideas to consider to reduce the risks:
CannabisNo amount of Cannabis (marijuana) has been proven to be safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding or chestfeeding. Stopping all cannabis product use while breastfeeding or chestfeeding is the safest option for your baby. No matter how cannabis is used, cannabis compounds are stored in body fat and can be passed to your baby through your milk. These chemicals are slowly released over time (up to 30 days) which means that “pumping and dumping” does not work. Some research reports that babies exposed to cannabis have slower motor development, reduced muscular tone, and poor sucking. If you consume cannabis and need help to reduce your consumption, or would like help quitting, please speak to your health care provider. AlcoholAlcohol passes into your milk. Alcohol is not stored in milk, instead it enters and exits according to your blood alcohol levels. Once alcohol is out of your blood, it will be out of your milk. Generally, it takes two hours for an average woman to clear the alcohol from one standard alcoholic drink. The safest choice is not to drink any alcohol while breastfeeding. If you are thinking about drinking alcohol occasionally while breastfeeding or chestfeeding, follow these tips to reduce risks to your baby:
Heavy alcohol consumption can put you and your baby at risk by:
Visit La Leche League International’s Drinking alcohol and Breastfeeding webpage for common questions about alcohol and breastfeeding, and recommendations supported by the evidence. |