Food skills
Food literacy
Food literacy is a broad term and involves:
- Knowing about food and where it comes from using trustworthy information.
- Food decisions and making food choices that work for you and your family's eating patterns.
- Systems and environments such as our community connections, cultures, traditions and where we live all play a role in the food we eat.
- Food skills and feeling confident in the kitchen, and shopping for, preparing, and eating food safely.
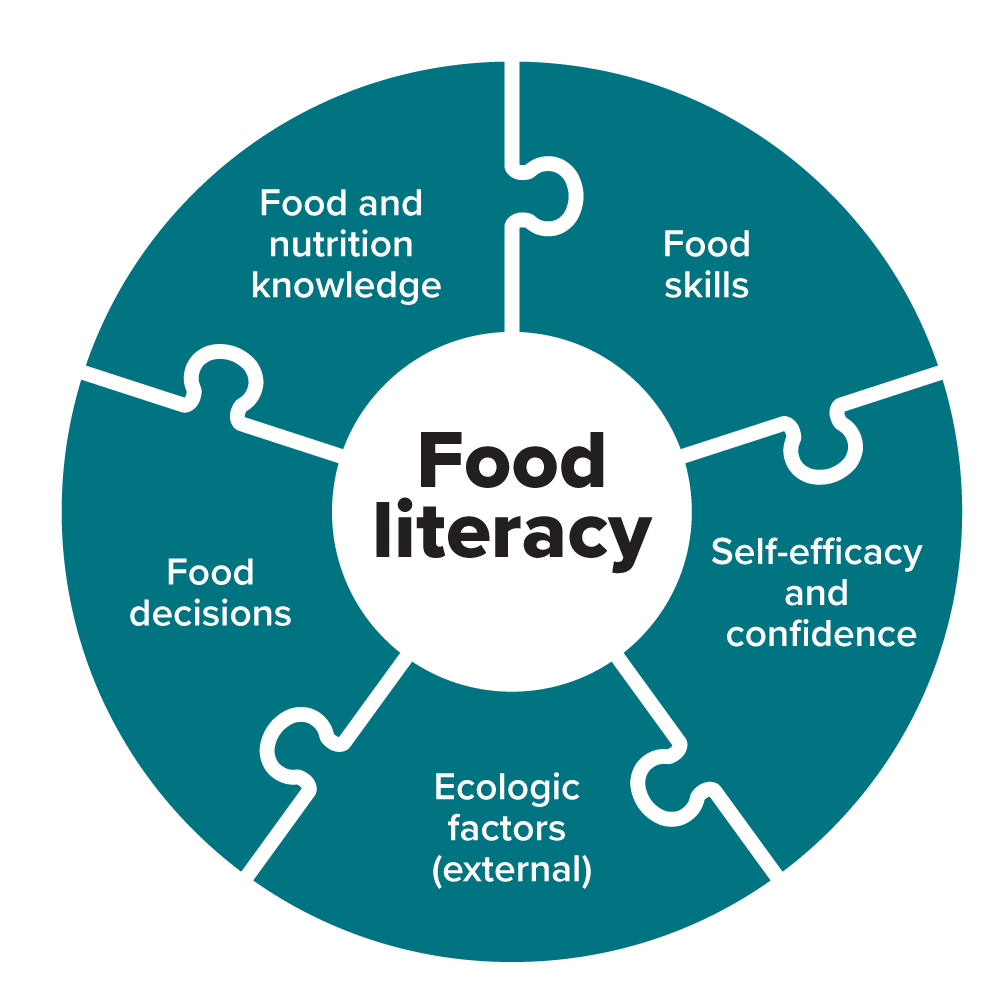
| Food literacy diagram - text description |
|
Planning your meals
Planning meals ahead of time can have big benefits like preventing food waste, helping you save money and time, and allowing you to prepare tasty and balanced meals.
There’s no right or wrong way to plan meals. Starting small and planning for just a few days can go a long way!
Decide what to eat |
|
When you are planning your meals it can be helpful to think about:
|
Make a shopping list |
|
Resources |
|
Grocery shopping
How you grocery shop affects what you eat, how much you spend and can make it easier to prepare foods.
Saving money while grocery shopping |
To help you save money:
|
Reading food labels |
|
Reading the Nutrition Facts Table can make it easy to compare similar foods and see which foods have a little or a lot of a certain nutrient. How to use food labels to make healthier choices - Canada's Food Guide What to look for on food labels
For more tips, here are 20 Ways to Save Money on your Groceries. |
Food safety at the grocery store |
|
Remember, food safety begins at the grocery store:
|
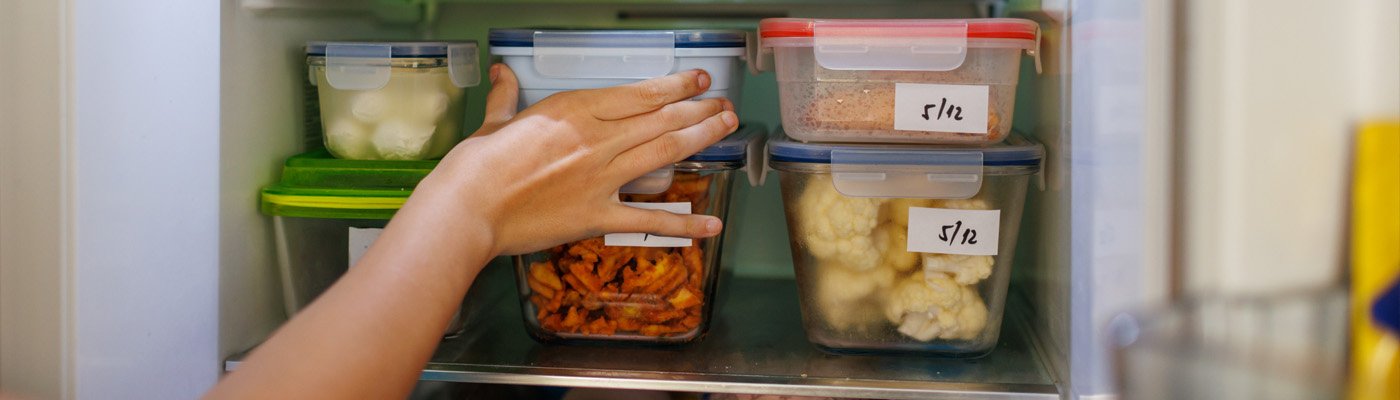
Storing food safely and making good use of leftovers
Storing food safely |
Storing your food and using leftovers safely is important to keep food fresh, avoid food waste and save money. Check out these helpful resources for tips on proper food storage:
Safe refrigerated food diagram - text description
Tips
|
| Best before versus expiry dates |
|
| Leftovers |
For more ideas, check out this Meal Planning Using Leftovers resource. |
Preparing meals
Using recipes |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Many people start with a recipe when they’re preparing meals. There are lots of easy recipes online, or you can find one that you’re interested in and modify it to suit food you have on hand and what you like to eat. Resources for using recipes: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common kitchen items and terms |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Putting a meal together |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
You can also put together a meal based on what you already have in the kitchen using the plate method. Consider what sources of protein, grains, and fruits and vegetables you have that could go together.
Canada's food guide plate - text description The Canada’s food guide plate shows the proportions of foods on a plate for healthy meals or snacks.
Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cooking techniques |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
After you’ve gathered your ingredients, the next step is preparing these foods, which might involve washing or rinsing, peeling, cutting, etc. Watch our helpful videos for more food preparation techniques. Did you know that you don’t need to have fancy kitchen equipment or even an oven to cook? You can prepare food using a variety of methods and tools. Here are some common cooking techniques and examples of equipment that you can use: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cooking different foods |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cooking doesn’t have to be complicated; you can make a new meal by simply adding a new vegetable like frozen peas into ramen or adding a new protein like lentils to tomato sauce. Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Save time and effort in cooking |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cooking can be a lot of effort, but you can make it easier by preparing foods in advance and cooking extra for leftovers. Here are some tips:
Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cooking for one or two |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Some recipes might seem like too much food when you’re cooking for one or two. Check out these resources on adjusting your recipes so you aren’t eating the same food all week. Resources |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preparing meals for specific diets |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lots of people need to adjust recipes based on food allergies, health conditions, or personal preferences. Sometimes this can be as simple as swapping out or leaving out an ingredient or may require more work to avoid cross-contamination with allergens. Here are some common special diets and how to adjust for them:
The information provided is general in nature and does not replace personalized therapeutic nutrition recommendations from a registered health-care provider. If you have specific dietary needs or health concerns, consult a qualified professional for individualized advice. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Food safety |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stay safe while preparing meals by keeping clean tools and a clean work surface, handling food safely and keeping foods at appropriate temperatures to avoid bacteria growth. Avoid food-borne illness at home:
Resources: |
Recipes
Need some cooking inspiration? Here are a variety of tasty and nutritious recipes for you and your household.
Recipe resource guide |
|
Simple and quick recipes |
|
Recipes using leftovers |
|
Recipes using seasonal produce |
|
Plant-based recipes |
|
Recipes to increase vegetables |
|